-
When it comes to commercial HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, chillers play a key role in keeping large buildings and industrial spaces cool. They remove heat from a building and transfer it elsewhere, making them essential for energy efficiency, comfort, and operational reliability.
There are two main types of chillers: Air-Cooled and Water-Cooled. Choosing the right one for your facility can help reduce energy costs, improve performance, and extend system lifespan.
-
What Is a Chiller?
A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid, usually water or a refrigerant, through a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle. This cooled liquid then cools air or equipment in commercial and industrial spaces.
Chillers are commonly used in:
• Office buildings
• Hospitals
• Shopping malls
• Manufacturing plants
• Data centers
-
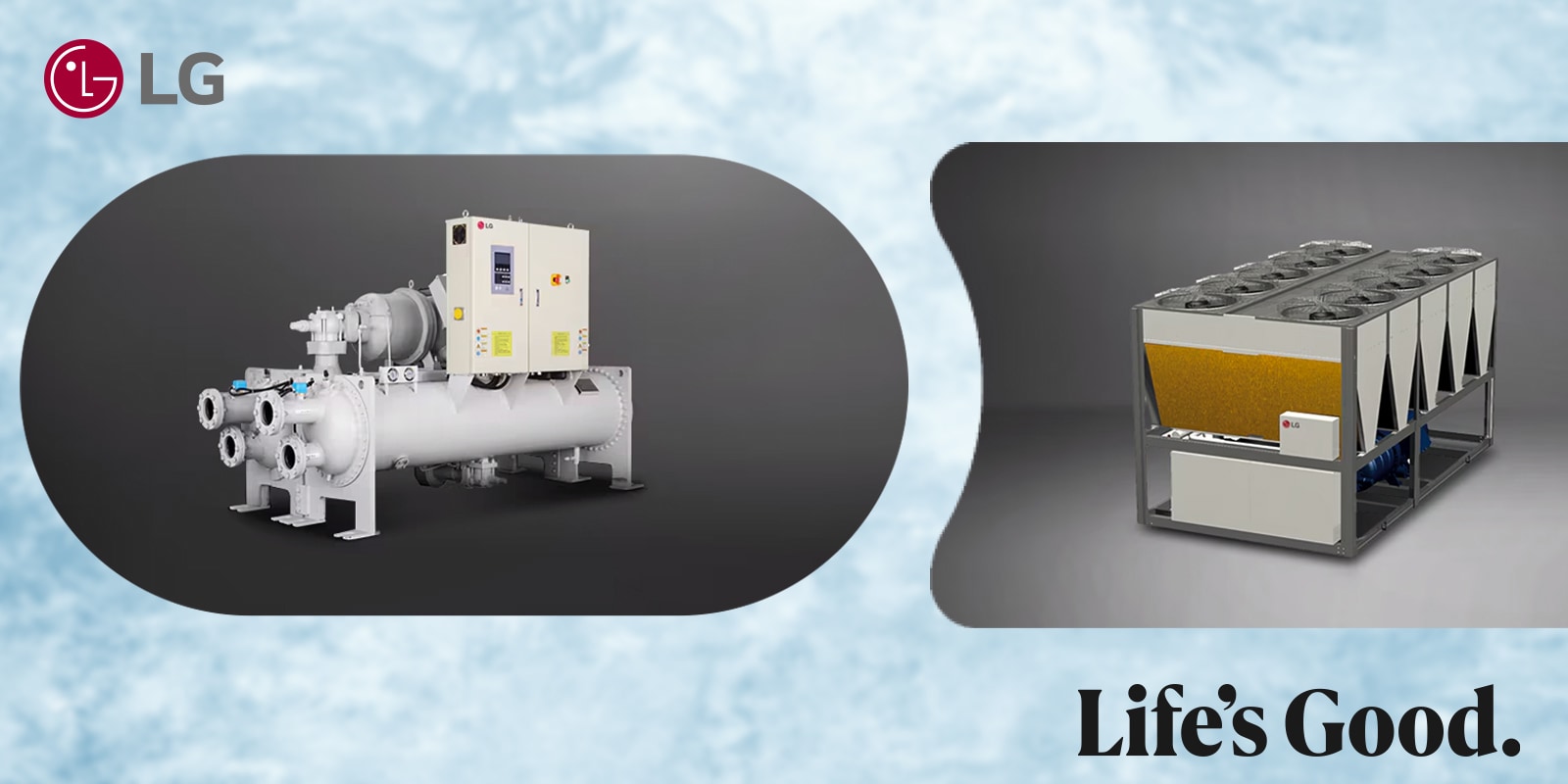
What Is an Air-Cooled Chiller?
An Air-Cooled Chiller uses air to remove heat from the system. Fans blow air over the condenser coils to cool the refrigerant.
Key components:
• Compressor
• Condenser coil
• Expansion valve
• Evaporator
• Fans
Common uses:
• Small to medium-sized buildings
• Facilities without access to a cooling tower
• Outdoor installations
Learn more: Air-Cooled Chillers by LG
-
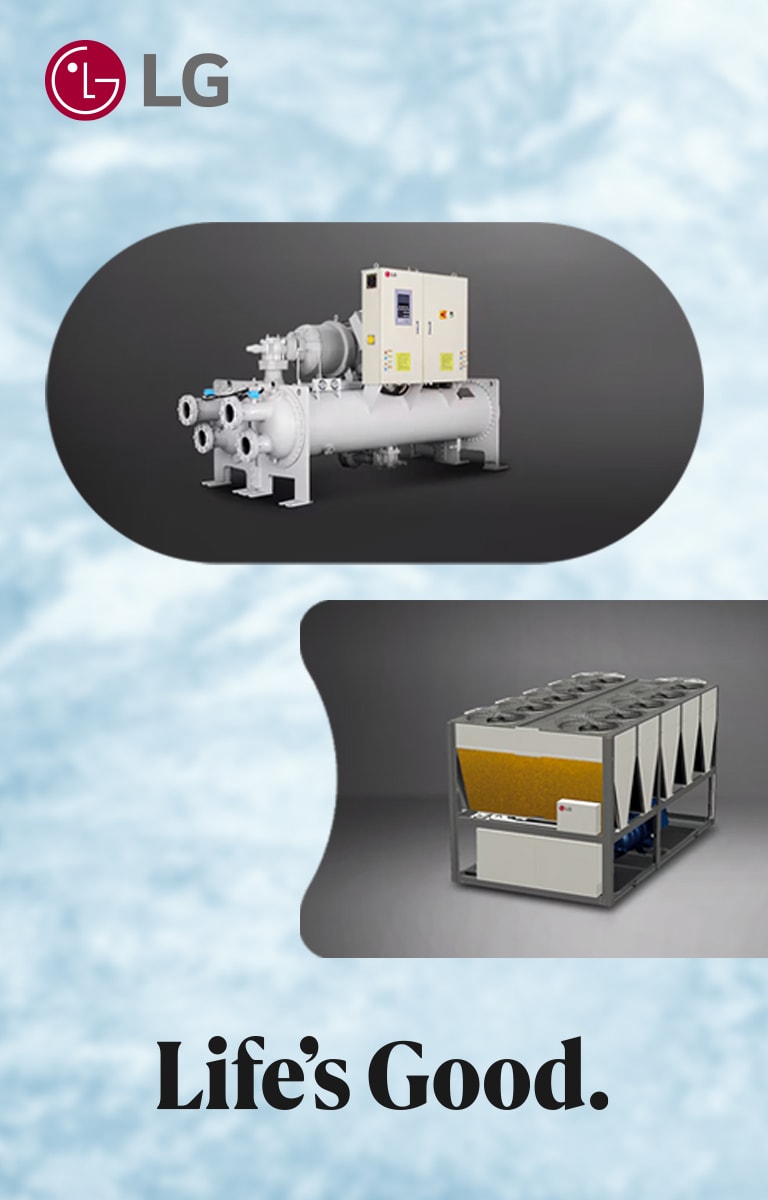
What Is a Water-Cooled Chiller?
A Water-Cooled Chiller uses water from a cooling tower to remove heat from the system. It is typically more efficient than an air-cooled system, especially for larger facilities.
Key components:
• Compressor
• Shell-and-tube condenser
• Expansion valve
• Evaporator
• Cooling tower and water pumps
Common uses:
• Large commercial buildings
• Industrial facilities
• Installations with space for indoor equipment and a cooling tower
Explore: LG Centrifugal Chillers
-
Air-Cooled vs Water-Cooled Chillers: A Quick Comparison
|
Feature |
Air-Cooled Chiller |
Water-Cooled Chiller |
|
Installation Cost |
Lower |
Higher (includes cooling tower & plumbing) |
|
Energy Efficiency |
Lower in hot climates |
Higher overall |
|
Cooling Performance |
Good for small to medium loads |
Excellent for large and consistent loads |
|
Maintenance |
Less frequent and simpler |
More complex, includes water treatment |
|
Space Requirements |
Can be installed outdoors |
Needs indoor space and cooling tower space |
|
Lifespan |
15–20 years |
20–30 years |
|
Noise Level |
Generally noisier |
Quieter indoor operation |
|
Water Usage |
None |
High |
-
Pros and Cons
Air-Cooled Chillers
Pros:
• Easy to install and relocate
• No water usage
• Lower initial cost
Cons:
• Lower energy efficiency
• Higher noise levels
• Affected by outdoor temperatures
Water-Cooled Chillers
Pros:
• High efficiency, especially for large buildings
• Quiet operation
• Longer lifespan
Cons:
• Higher upfront and maintenance costs
• Requires access to clean water
• Needs more space and technical infrastructure
-
How to Choose the Right Chiller for Your Facility
When choosing between an air-cooled and a water-cooled chiller, consider the following:
• Building size and cooling load: Larger buildings often benefit from water-cooled chillers.
• Indoor vs. outdoor space: Air-cooled units can be placed on rooftops or open areas.
• Access to water: Water-cooled chillers require a stable and clean water source.
• Energy and water costs: Consider long-term savings vs. upfront expenses.
• Climate: In very hot temperatures, water-cooled chillers often perform better.
• Maintenance capabilities: Water-cooled systems need more ongoing care.
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between air cooling and water cooling?
Air cooling uses fans and air to release heat, while water cooling uses water and a cooling tower for better efficiency in large-scale systems.
What is the difference between HVAC and a chiller?
HVAC is a broad system that includes heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. A chiller is part of the HVAC system and is specifically responsible for cooling.
Which type of chiller is best?
It depends on your building size, location, and cooling needs. Air-cooled chillers are great for small to medium spaces, while water-cooled chillers are better for large-scale cooling.
-
Conclusion
Choosing the right chiller is a big decision for any facility manager or developer. Whether you're upgrading an old system or planning a new build, LG’s innovative chiller solutions are designed to offer high performance, reliability, and efficiency.
Discover LG’s full range of chillers here: LG Business Chillers