We use cookies, including cookies from third parties, to enhance your user experience and the effectiveness of our marketing activities. These cookies are performance, analytics and advertising cookies, please see our Privacy and Cookie policy for further information. If you agree to all of our cookies select “Accept all” or select “Cookie Settings” to see which cookies we use and choose which ones you would like to accept.
HELPFUL HINTS
What is a Heat Pump Dryer? Dryer Comparison and Pros & Cons
Discover information on heat pump dryer technology and how it is different from the other types of dryers available.
Traditional electric and gas dryers have been in use for decades, but they are becoming less popular due to their high energy consumption and negative impact on the environment. Heat pump dryers have emerged as an energy-efficient alternative to traditional dryers. This article will discuss what a heat pump dryer is, how it works, and how it compares to other types of dryers.
Heat Pump Dryer
What is a heat pump dryer?
A heat pump dryer is a type of dryer that uses a heat pump to dry clothes. Introduced to the market in the early 2000s, heat pump dryers are known for their high energy efficiency and low carbon footprint. They are also known to take longer to dry clothes compared to traditional vented dryers, which can be a disadvantage for some users.1
How does a heat pump dryer work?
Electric and gas vented dryers use electric or gas heaters to heat the air inside the dryer drum and blow it through the clothes to make the moisture in them evaporate. This heated air is then vented outside the dryer, which can cause heat loss and wasted energy.
In contrast, heat pump dryers use a closed-loop system that recirculates air through the drum. After condensing moisture out of the air, the warm air is reheated to continue the drying process without being vented.
This means that heat pump dryers use less energy and waste less heat, meaning they are better for the environment.
LG’s Heat Pump Dryer Technology
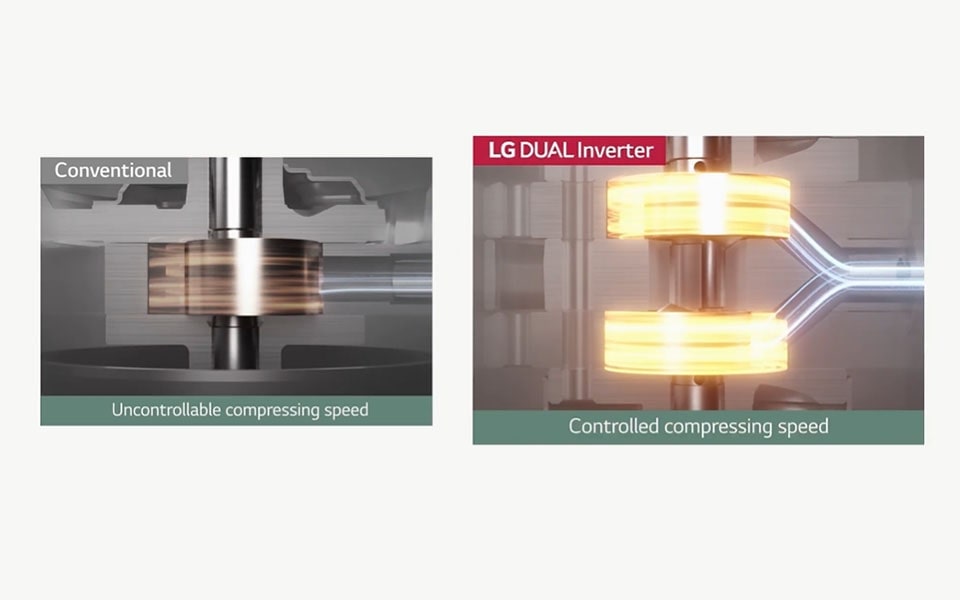
LG's heat pump dryers use DUAL Inverter Heat Pump technology. Two cylinders work together, using a range of circulation speeds, from very fast to slow, to dry the clothes inside the dryer drum faster than would be possible with LG’s conventional heater dryers.2
Heat Pump vs Condenser Dryer
Heat Pump Dryer Pros and Cons
Pro 1: Energy-efficient dryer
Heat pump ventless dryers are highly energy efficient, which helps homeowners reduce energy consumption and utility bills. These dryers use a heat pump system to reuse heated energy during the drying cycle, which means they consume less energy than traditional vented dryers.
According to Energy Star, a heat pump dryer can save up to 28% in energy costs compared to a standard dryer. As a result of the LG internal test, the LG 27-inch Heat Pump dryer can save up to 58% in energy costs compared to the electric vented dryer, and the LG 24-inch Heat Pump dryer can save up to 65% in energy costs compared to the condenser dryer.345
Pro 2: Fabric protection
Heat pump dryers protect fabric better than LG’s conventional heater dryers by using a low-temperature drying process that reduces the risk of shrinking or damage from high temperatures.6
Pro 3: No dryer vent installation
Unlike traditional dryers, heat pump dryers do not need a vent installed, to release hot and humid air outside. They reduce the risk of fire, thanks to their ventless system. So, Heat pump dryers have better safety features than traditional dryers. And they use a closed-loop system to dry clothes, making them more convenient for apartments or homes without proper ventilation available. This feature also makes them a flexible option for any living space, as they can be used in various locations around the home.
Cons
There are also some drawbacks to heat pump dryers. They are more expensive than traditional dryers, which can be an obstacle for some consumers. However, it is necessary to consider future maintenance costs such as the amount to be rebated and the cost of installing an exhaust vent. Heat pump dryers can take longer to dry clothes than other dryers, which can be inconvenient for users who need to dry clothes quickly. LG's heat pump dryers feature a special dry mode, which allows users to choose between two drying options - Energy Saving and Time Saving. Energy Saving mode uses less energy and is ideal for drying smaller loads of clothes, while Time Saving mode is faster and better suited for larger loads.
Condenser Dryer Pros and Cons (Heater-Condensing)
Heater-Condensing dryers are a type of ventless dryer that uses an electric heater to remove moisture from the air. They work by heating air and passing the hot air through wet clothes, causing the moisture in them to evaporate into the air. The moist air is then passed through a condenser, where it is cooled, and the moisture is condensed into water. The water is then collected in a reservoir that needs to be emptied manually or pumped out.
Pros
Condenser dryers are more versatile than vented dryers because they do not need a venting system, so they can be placed in any room.
Cons
They typically have higher energy consumption than vented dryers and can take longer to dry clothes due to the need to remove moisture from the air inside the dryer. Due to running at high temperatures, both heater condenser and vented dryers can cause damage to clothing.
Gas vs Electric Dryer
Gas Clothes Dryer Pros and Cons (Vented Dryer)
Gas clothes dryers use natural gas or propane to generate the heat needed for drying clothes. The gas is ignited by an igniter and the hot air given off is circulated by a fan.
Pros
Gas dryers typically have higher upfront costs but lower operating costs over time.
Cons
Gas dryers require a dedicated gas line to supply constant fuel for heating and a venting system to remove exhaust gases. They are not suitable for homes without a gas line or proper ventilation. Gas dryers can be more dangerous than electric dryers because of the risk of gas leaks and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Electric Dryer Pros and Cons (Non Heat Pump, Vented)
Traditional electric vented clothes dryers use electricity to generate heat for drying clothes. An electric heating element converts electrical energy into heat, and a fan circulates the heated air.
Pros
Electric dryers are typically less expensive upfront than other dryers. This can make them a more affordable choice for families who are on a tight budget. They also have a higher heat output than gas dryers, meaning they can dry clothes more quickly. This makes them useful to people who need their clothes dried quickly, such as large families or people with busy schedules. over time.
Cons
Electric vented dryers require a dedicated electrical circuit and a venting system to remove the moist air. They are suitable for most homes but can be less energy-efficient than heat pump dryers, which are the more technologically advanced form of electric dryers.
Which type of dryer is the best?
The best type of dryer for you is a matter of preference. Traditional electric dryers are inexpensive and dry clothes quickly, making them a viable choice for those who looking for inexpensive products, need to run the dryer multiple times a day, and require fast drying. On the other hand, for those who prioritize maintenance costs, have installation constraints, and have experienced clothes shrinkage, a heat pump dryer would be the better choice.
Heat pump dryers are an innovative and energy-efficient alternative to traditional dryers. They have lower operating costs and a smaller carbon footprint than other dryers. LG's heat pump dryer technology is designed to provide users with a more energy-efficient and effective drying experience. With innovative features like the DUAL Inverter HeatPump and auto cleaning condenser, LG's heat pump dryers offer a range of benefits that make them a top choice for consumers who want a high-quality and reliable dryer. When choosing a dryer, it is important to consider your needs and budget to decide which type of dryer is best for you.
1. *When compared with comparable vented dryer, based on intertek testing in normal cycle, 8.45 lb. load, WKHC202HBA vs. vented Dryer DLEX4000W (December 2021).
2. Tested by Intertek, Normal cycle with Normal Dry Mode compared to conventional Normal cycle with default option (DLHC1455W vs. DLEC888W), 8.45 lb. of 57.5% initial moisture content DOE load (January 2021).
3. Tested by Intertek, Normal cycle with default option, 8.45 lb. of 57.5% initial moisture content DOE load.
4. Tested by Intertek, Normal cycle with Normal Dry Mode compared to conventional Normal cycle with default option (DLHC1455W vs. DLEC888W), 8.45 lb. of 57.5% initial moisture content DOE load (January 2021).
5. There may be differences in the actual use environment.
6. When compared with comparable vented dryer, based on intertek testing in normal cycle, 8.45 lb. load, WKHC202HBA vs. vented Dryer DLEX4000W (December 2021).100% wool fabric cloth (December 2021).
Featured product
- Newest
- Most Popular