We use cookies, including cookies from third parties, to enhance your user experience and the effectiveness of our marketing activities. These cookies are performance, analytics and advertising cookies, please see our Privacy and Cookie policy for further information. If you agree to all of our cookies select “Accept all” or select “Cookie Settings” to see which cookies we use and choose which ones you would like to accept.
LG LAB
Guide to choosing the right HVAC heating and cooling system
- Compare different types of home heating and cooling systems based on budget, size, power load, noise level and the layout of your home
- Learn how to choose the right HVAC system for an apartment or a house
- Dive into the differences between geothermal and air source options and the pros and cons of each HVAC type
- Discover if you need a basic fixed-speed inverter or a heat pump for your home
Choosing the right HVAC system could seem confusing at first, especially with the wide range of technologies now available. Whether you are selecting equipment for a flat, a detached house, or a business property, knowing which heating and cooling systems work best for your needs will affect comfort, running costs and energy use.
This guide will help you make a confident decision by comparing some of the most popular types of HVAC technology for any home.
How to know which HVAC system is best for you
Selecting the best heating and cooling systems depends on your personal circumstances. No single option suits everyone, but by examining your budget, property size, comfort preferences, and smart features, you can make a well-informed choice.
In general, you can see which HVAC heating and cooling system you need by comparing these key benefits and draw backs:
We will dive into the detailed differences between each of these systems further in the article, which will also compare standard HVAC systems based on your preferred shopping criteria:
Based on budget
Your available budget often determines which systems are suitable. While low-cost models can be tempting, it is worth comparing upfront cost against lifecycle value. High-efficiency heat pumps and inverter systems usually reduce electricity bills over time, offsetting their initial cost.
Government rebates and local incentives increasingly encourage the use of home heating and cooling systems that deliver energy efficiency, such as air-source heat pumps.1 These can make premium systems like LG’s inverter heat pumps more affordable. Spreading payments through financing also helps homeowners move towards more efficient solutions without heavy initial expenses.
Based on size, load and orientation
Your home’s scale and overall layout also play a key role. Professionals can calculate your heating and cooling load by examining insulation, windows, and climate. A smaller apartment may work best with a ductless mini-split system, which allows you to control temperature in individual rooms. LG’s Multi V series is a good example, offering multiple indoor units connected to a single outdoor compressor.
Larger homes with multiple floors or open-plan spaces often need central or multi-zone heating and cooling systems. Ducted options work well in new builds or major renovations, while ductless or hybrid setups suit retrofits where installing ducts would be difficult or costly.2
Based on quietness and noise
Noise levels can make a huge difference to comfort. Inverter systems tend to be much quieter than traditional units because they operate continuously at variable speeds instead of switching fully on and off.3 When comparing heating and cooling units, look for the indoor and outdoor sound ratings in decibels. Placement of the outdoor unit also matters, especially in densely built areas or flats with shared walls.
Based on smart connectivity and controls
Modern home heating and cooling systems often feature smart connectivity that lets you monitor and control performance from your phone. LG’s ThinQ smart app, for example, allows remote scheduling, temperature adjustment, and energy reporting. If you use smart thermostats, ensure the HVAC system is compatible. Intelligent diagnostics can even help reduce the frequency of heating and cooling repair visits.
Make the right HVAC decision for your home or building
The following list provides guidance on how to find which heating and cooling systems would work best for your home:
- Assess your climate, insulation and electricity costs.
- Establish a budget and preferred payback timeframe.
- Choose between ducted, ductless, or hybrid distribution.
- Compare inverter and fixed-speed systems for efficiency.
- Select trusted brands such as LG for reliability and technology.
- Get a professional load calculation and quotation.
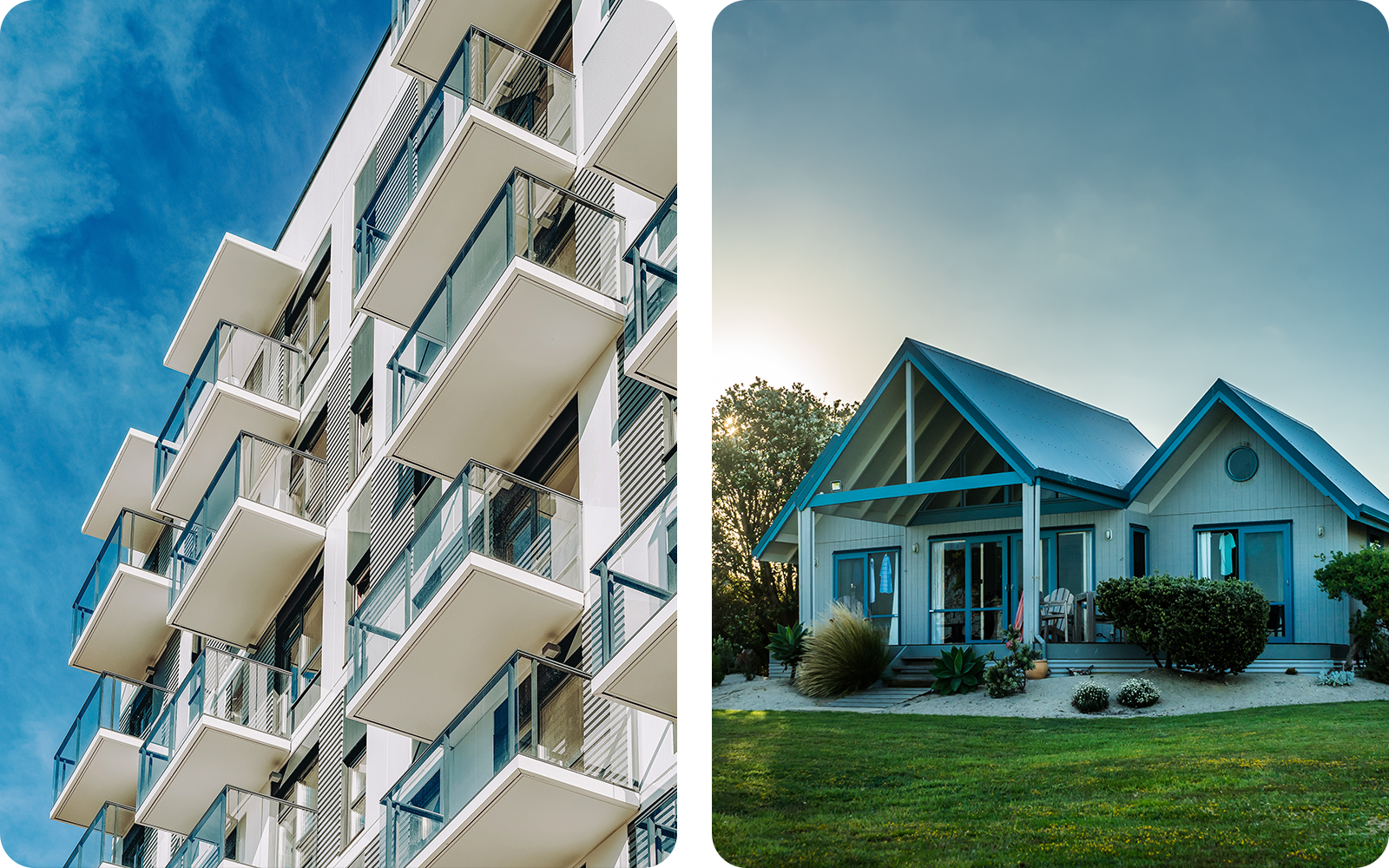
Choosing HVAC for an apartment versus a house
Unique constraints in apartments
Apartments often come with space and noise restrictions. There may be no outdoor space for large condensers, and shared walls can limit installation options. Many flats also have limited electrical capacity and little or no ductwork. This makes compact heating and cooling units ideal for apartment living.
Typical system choices for apartments
Popular choices include ductless mini-split heat pumps, through-the-wall units, and compact inverter systems. LG’s multi-split inverter systems allow multiple indoor units connected to one outdoor compressor, offering individual temperature control without requiring ducts.
Considerations for houses
Houses typically have greater heating and cooling demands, larger conditioned spaces, and the option for outdoor installations. This allows for centralised home heating and cooling systems or multi-zone configurations. Properties with sufficient land can even consider geothermal or hybrid systems for higher long-term efficiency.
Which LG systems suit each setting
For apartments, some inverter heat pumps can provide flexible comfort with minimal space requirements. And for houses, ducted inverter heat pumps deliver especially efficient multi-zone climate control. Both options show how well-designed heating and cooling systems could adapt to different living environments.
Do I need a heat pump?
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump transfers heat rather than creating it through combustion. It reverses its operation depending on the season, heating in winter and cooling in summer.4
Benefits of a heat pump
Generally, heat pumps are considered to be among the best heating and cooling systems for efficiency, delivering three to five times more heat energy than the electricity they consume. They provide both heating and cooling in one system, lower carbon emissions, and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Cold-climate inverter heat pumps maintain reliable output even in freezing temperatures.
When a heat pump may not be ideal
In very cold areas, performance can drop if the system is undersized or lacks a backup heat source. High electricity costs or poor insulation can also limit cost-effectiveness. In such cases, a hybrid solution or additional insulation may improve performance.
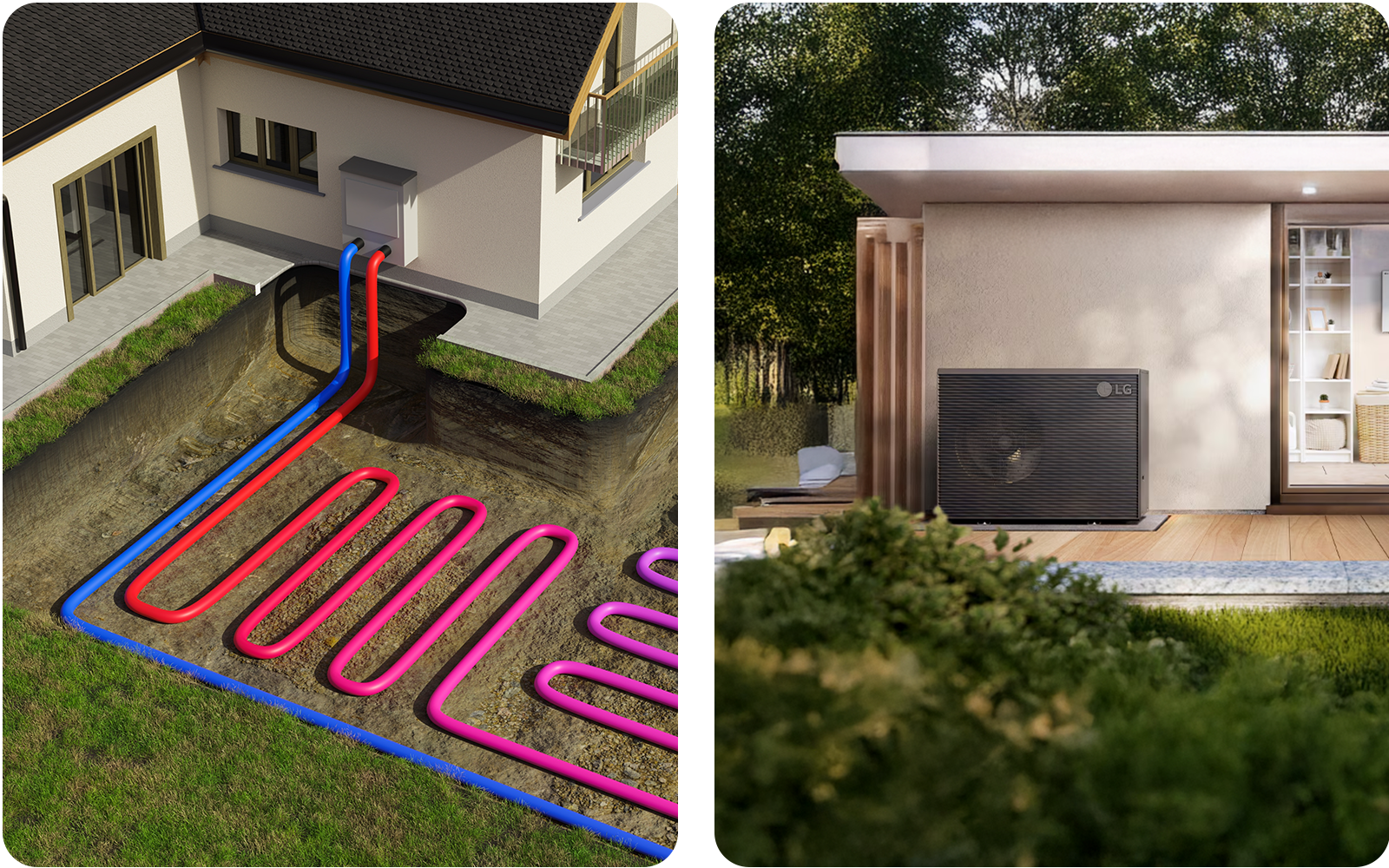
Geothermal versus air source heat pumps
Air source heat pumps
Air source models draw heat from outdoor air and release it indoors. They are simpler to install and require only an outdoor and indoor unit. Efficiency can fall during very cold weather, but modern inverter models handle most climates well.
Geothermal heat pumps
Geothermal systems, also known as ground-source heat pumps, use the stable temperature of the ground or groundwater through buried loops. They maintain steady performance year-round and last for decades, but require a higher initial investment and sufficient land for installation.5
Side-by-side comparison
Die Inverter-Produktreihe von LG umfasst sowohl Kanalsysteme als auch kanallose Systeme für die Nutzung in Wohnräumen mit intelligenter Kommunikation und Fernsteuerung. Für größere Gebäude bietet LG Inverter-Scroll-Chiller an, die diese Vorteile auf gewerbliche Heiz- und Kühlumgebungen ausweiten.
When geothermal makes sense
Geothermal systems suit new builds, properties with available land, or homeowners planning long-term occupancy. They perform well in very cold climates where air source units may struggle.
LG and geothermal or hybrid options
LG focuses mainly on advanced air-source inverter technology. Some hybrid configurations can combine these systems with ground loops, though this is less common in residential settings.
*LG does not offer geothermal heating and cooling systems; related information is for comparison only
Do I need an inverter system?
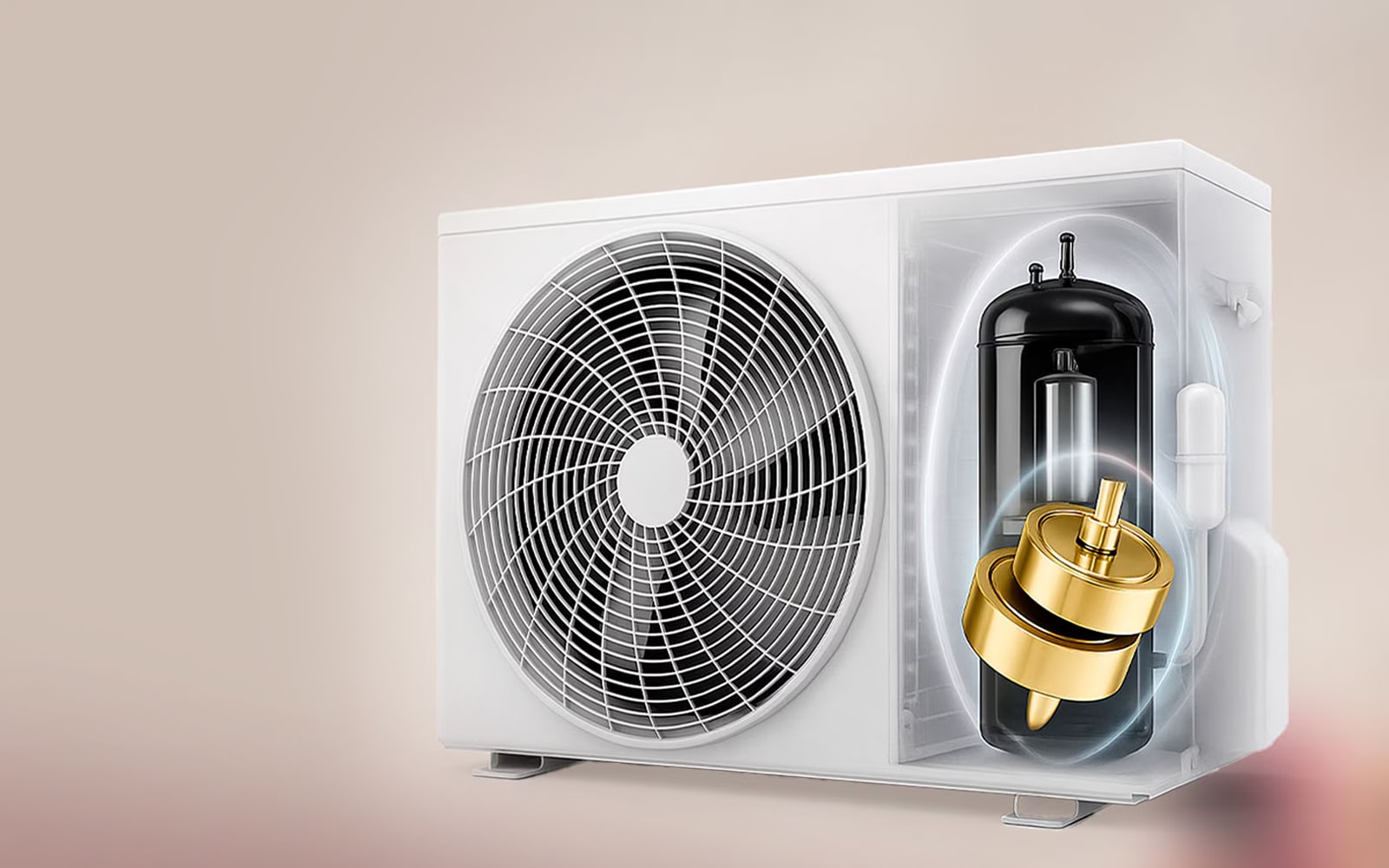
What is an inverter compressor?
An inverter compressor adjusts its speed to match the heating or cooling demand. This continuous adjustment avoids the energy waste of switching fully on and off, leading to smoother operation and better temperature control.6
Advantages of inverter systems
- Consistent temperature and improved comfort
- Reduced energy consumption, especially in mild weather
- Quieter operation and fewer mechanical stresses
- Compatibility with smart thermostats and automation
Short- vs. long-term considerations
Inverter systems cost more initially and include more complex electronics. They require compatible indoor components and control systems, but the long-term energy savings for inverter air conditioners usually outweigh these drawbacks.7
Advantages of inverter systems
- Consistent temperature and improved comfort
- Reduced energy consumption, especially in mild weather
- Quieter operation and fewer mechanical stresses
- Compatibility with smart thermostats and automation
Advantages of inverter systems
- Consistent temperature and improved comfort
- Reduced energy consumption, especially in mild weather
- Quieter operation and fewer mechanical stresses
- Compatibility with smart thermostats and automation
Short- vs. long-term considerations
Inverter systems cost more initially and include more complex electronics. They require compatible indoor components and control systems, but the long-term energy savings for inverter air conditioners usually outweigh these drawbacks.7
LG’s inverter offerings
LG’s inverter product range includes both ducted and ductless solutions for residential use, featuring intelligent communication and remote control. For larger buildings, LG offers inverter scroll chillers that extend these benefits to commercial heating and cooling environments.
Inverter versus basic (fixed-speed) heat pump systems: pros and cons
When choosing between inverter and fixed-speed heat pump systems, understanding the pros and cons of each option will help you select the best solution for your home. Modern heating and cooling systems increasingly rely on inverter technology because it provides smoother, more efficient performance. However, both systems have their own strengths and limitations depending on your needs and budget.
Pros and cons of inverter systems
Advantages of inverter systems
- Greater energy efficiency
One of the main advantages of inverter systems is their ability to regulate output continuously. Instead of turning on and off, the compressor adjusts speed to match your home’s temperature requirements. This precision means less wasted energy and lower electricity bills over time.7
- More consistent comfort
Inverter compressors maintain an even temperature without the sharp fluctuations found in basic systems. This steady performance ensures a more comfortable indoor environment, particularly during changing weather conditions.
- Quieter operation
Because inverter systems avoid sudden stop-and-start cycles, they operate far more quietly. This makes them ideal for bedrooms, offices, and flats where noise reduction is important.
- Longer system lifespan
The gradual operation of an inverter compressor places less stress on mechanical parts. This reduced wear can lead to longer service life and fewer heating and cooling repair calls over the years.
- Smart control compatibility
Many inverter systems, such as LG’s ThinQ-enabled models, integrate easily with smart thermostats and home automation platforms. These allow remote scheduling, monitoring, and energy tracking for improved convenience and efficiency.
Disadvantages of inverter systems
- Higher upfront cost
Inverter technology typically costs more to purchase and install than a basic fixed-speed system. However, the investment often pays off through energy savings and reduced maintenance over time.8
- More complex electronics
The internal components and control systems of inverter units are more advanced. While this allows precision and efficiency, it may also require specialised servicing or parts if a repair is needed.
- Dependence on compatible components
Inverter systems work best when paired with matching indoor units and control interfaces. Using incompatible parts can limit performance or disable certain smart features.
Pros and cons of fixed-speed systems
Advantages of fixed-speed systems
- Lower initial cost
Fixed-speed heat pumps are generally less expensive to buy and install. This makes them appealing for smaller properties or short-term use where the lower upfront price is the priority.
- Simpler design and maintenance
The technology behind fixed-speed systems is straightforward. Many technicians can service these units quickly, and spare parts are usually easy to source.
Disadvantages of fixed-speed systems
- Lower energy efficiency
Fixed-speed compressors run at full power until the desired temperature is reached, then switch off completely. This on-off cycling wastes energy and increases running costs.
- Inconsistent comfort levels
Because they generally do not adjust output dynamically, fixed-speed systems often cause noticeable temperature swings and less precise climate control.
- Higher noise levels
Sudden compressor starts and stops can create noise, which may be disruptive in quiet areas or at night.
- Shorter lifespan and more wear
The repeated full-speed cycling places extra strain on components, potentially shortening the system’s overall life and increasing the likelihood of maintenance or heating and cooling repair work.
The best heating and cooling systems are those that fit your specific environment, comfort needs, and financial plan. Apartments may work best with ductless systems, while houses benefit from larger central or hybrid setups. Choosing between air-source and geothermal technologies depends on climate and available space, while inverter systems add efficiency and quiet comfort.
LG’s inverter-based solutions represent a reliable benchmark for modern home heating and cooling systems and even commercial heating and cooling applications. With proper design, installation, and maintenance, you can enjoy comfort, efficiency, and long-term peace of mind, confident that you have chosen which heating and cooling systems truly suit your home.
Life's Good!
1 European Commission for Energy 2025
2 Optimizing Heating and Cooling in New Build
3 LG inverter air conditioners operate between 19 dB (whisper quiet) and 58 dB. Sound pressure levels are tested in an anechoic chamber under ISO Standard 3745 and are the same in both cooling and heating modes. These values can increase due to ambient conditions during operation.
4 Performance is measured by the Coefficient of Performance (COP), Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF).
5 Department of Energy: Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs), take advantage of the constant temperature of the shallow earth (40°-70°F/4.5°-21°C) to efficiently exchange temperatures, heating homes in the winter and cooling homes in the summer.
6 Inverter technology uses a variable-frequency drive (VFD) that regulates the speed of the compressor motor.
7 LG Inverter air conditioners (US-Q242K*) save up to 70% more energy than LG non-inverter air conditioners (TS-H2465DA0). Initial Temperature (Outdoor 35°C, Indoor 33°C) / Setting Temperature (26°C) / Testing time (8 hours).
8 The compressor in an inverter AC adjusts its speed to maintain the desired temperature, instead of continuously cycling between on and off at full power.