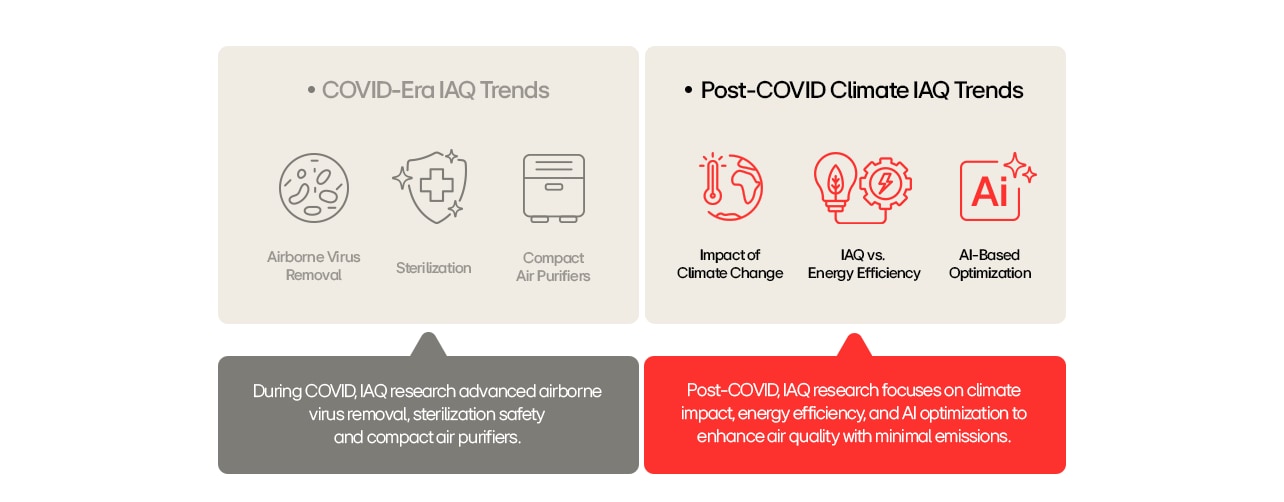
A: Efforts to improve indoor air quality (IAQ) have evolved beyond simply purifying the air—they now focus on balancing air quality with building energy efficiency. This shift became especially important after the pandemic, which highlighted the need for increased ventilation and air purification, potentially leading to higher energy consumption. As a result, recent research and technological development have aimed to achieve both improved IAQ and energy savings simultaneously.
To support these goals, the following areas of research and development have been actively pursued.
1. Smart ventilation control systems
– Analyzes indoor air quality data in real time—such as CO2 concentration, PM2.5, and VOCs—and activates the ventilation system only when necessary to prevent energy loss from excessive ventilation.
– When outdoor air is polluted, ventilation is temporarily paused or filtered before being introduced indoors, reducing energy loss while meeting IAQ standards.
2. Heat Recovery Ventilation and Energy Recovery Ventilation
– A technology that recovers the heat (or humidity) from indoor exhaust air to minimize energy loss when bringing in outdoor air—reducing cooling energy loss in summer and preventing heating energy loss in winter.
3. Low-power, high-precision IAQ sensor technology
– As IAQ sensor technology rapidly advances, it addresses previous issues such as high-power consumption and short lifespan found in conventional air sensors. Low-power semiconductor sensors have emerged as a key solution, enabling long-term, precise air quality monitoring while significantly improving energy efficiency.
4. AI-Based Energy and IAQ Optimization Control
– LG is developing air purifiers that use AI-powered sensors to check the air quality and automatically adjust how strongly the device runs. These smart features help keep the air clean without needing manual control.
5. Integrated Air Purification and Ventilation System
– A growing trend is the integration of previously separate systems—air purification (mainly for indoor air circulation and cleaning) and ventilation (mainly for outdoor air intake and exhaust)—into a single platform. This allows both systems to operate simultaneously or in coordination, reducing energy waste while effectively managing indoor air quality.