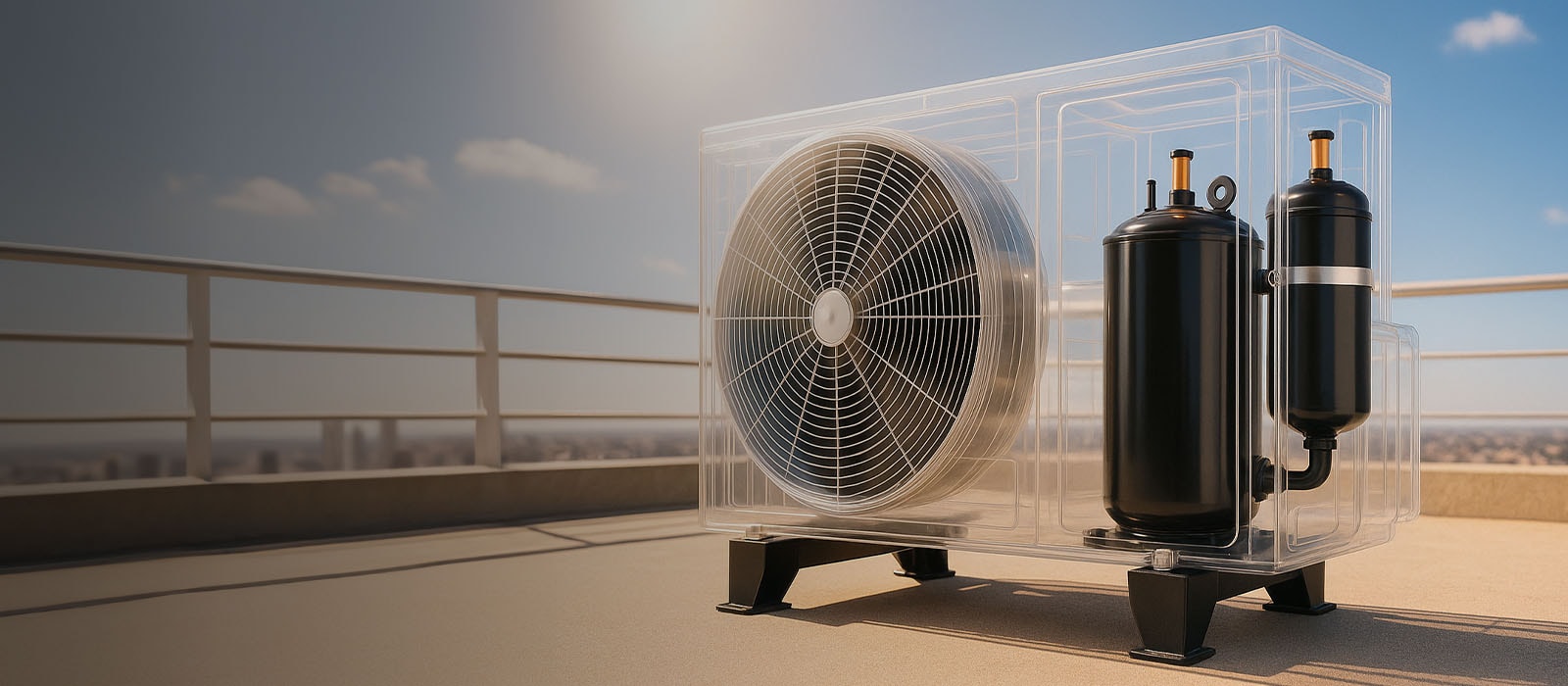
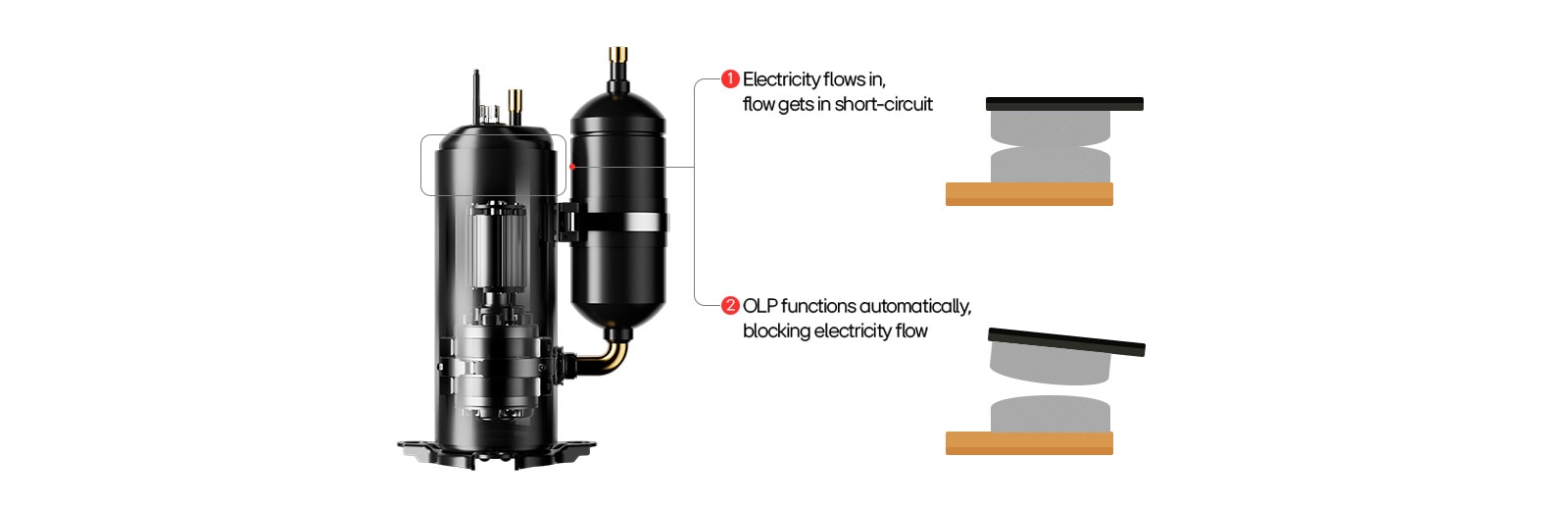
Protecting the entire compressor system, including the motor, is essentially protecting the compressor itself. The key to this protection is a component known as the overload protector. It serves to safeguard the compressor from damage caused by excessive internal motor temperature or electrical stress. When dangerous heat levels or excessive currents are detected, the overload protector cuts off power to the motor, effectively halting the compressor’s operation and preventing potential failure. In such cases, the compressor may restart after a delay of a few minutes, allowing the system time to stabilize and recover safe operating conditions.
The overload protector plays a crucial role in preemptively blocking factors that could harm the motor. It ensures that potential issues, such as electrical overloads or overheating, are addressed before they cause permanent damage. The effectiveness of this protection depends on how well the protector is matched to the motor’s design, which is often based on each manufacturer’s engineering expertise.
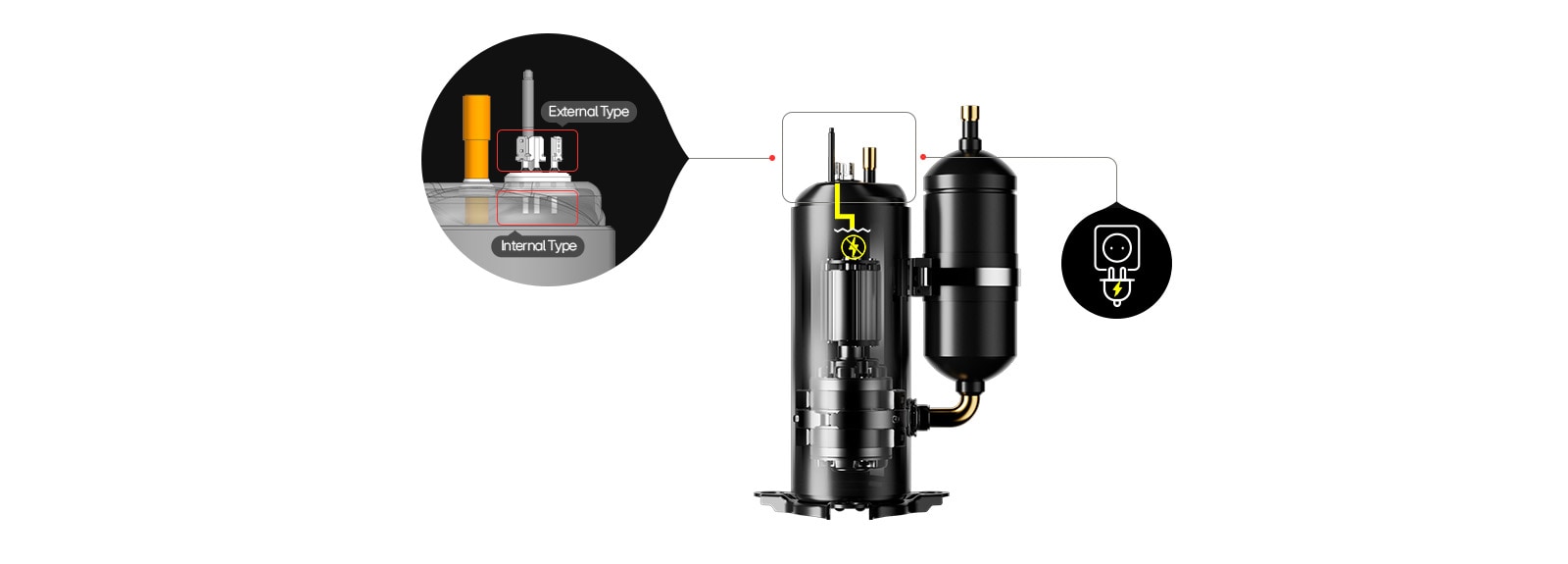
Overload protectors come in two main types:
1) External type: Easier to replace and maintain, but generally less sensitive due to its distance from the motor
2) Internal type: Built directly into the motor, offering better sensitivity and faster response, but harder to replace if damaged.