The warming of the Earth can be affected differently by different greenhouse gases. Global Warming Potential (GWP) is an index introduced to measure and compare the impacts of various greenhouse gases on global warming over a specific time. The period usually used for GWPs is 100 years but for gases with shorter lifetimes, an alternative of a period of 20 years is used.
Carbon dioxide is used as a reference gas because it has a long residence of time in the atmosphere and also has the greatest impact on global warming.
In particular, GWP is a measurement of the amount of energy that a ton of gas emissions will absorb in relation to a ton of carbon dioxide emissions over a given period. R-22, for instance, the most common refrigerant today, has a 100-year GWP of 1,810, nearly 2,000 times the potency of carbon dioxide, so one pound of R-22 has almost as much potency as a ton of carbon dioxide.2) Generally, the higher the GWP, the more the gas warms the Earth.
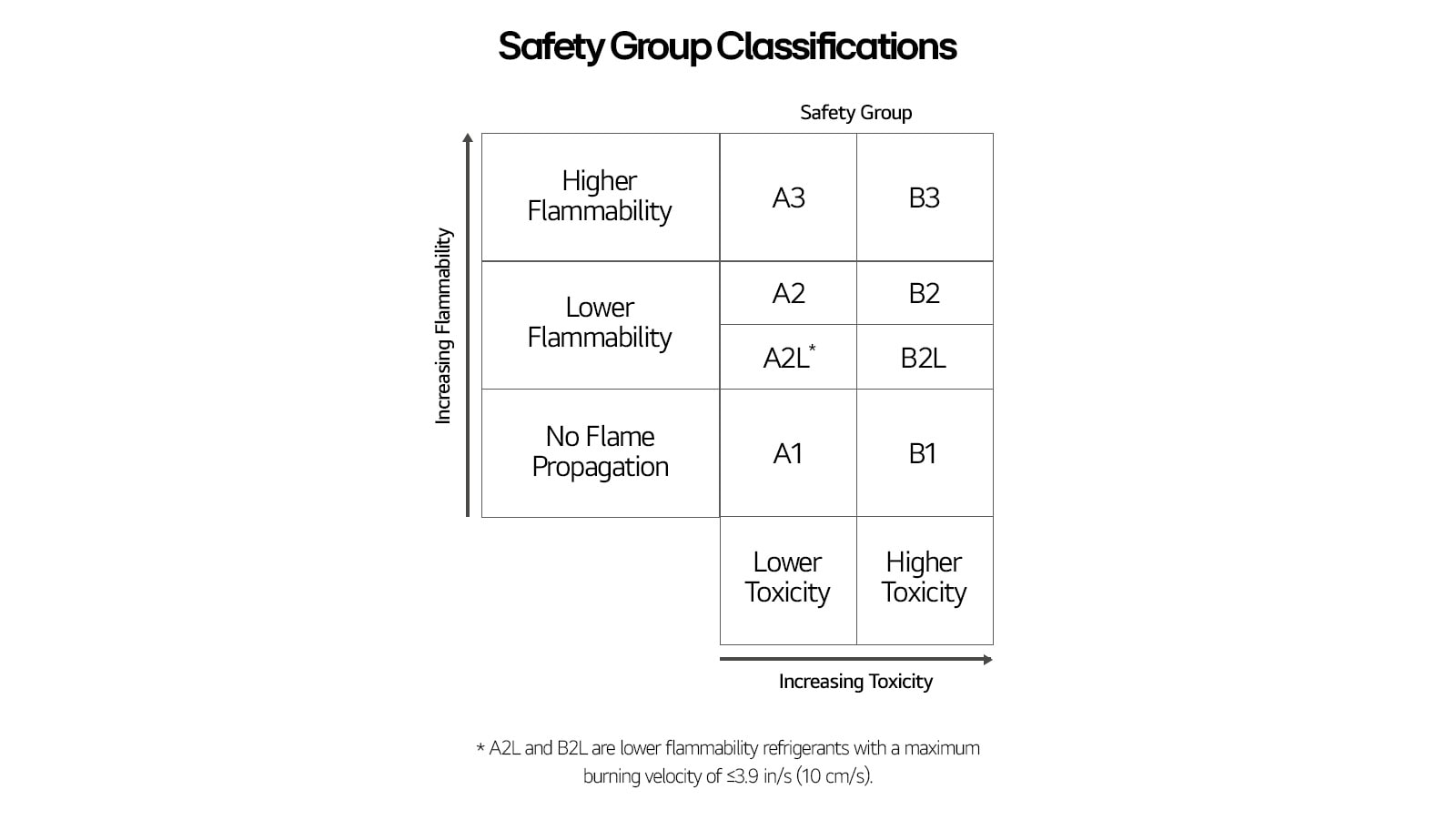
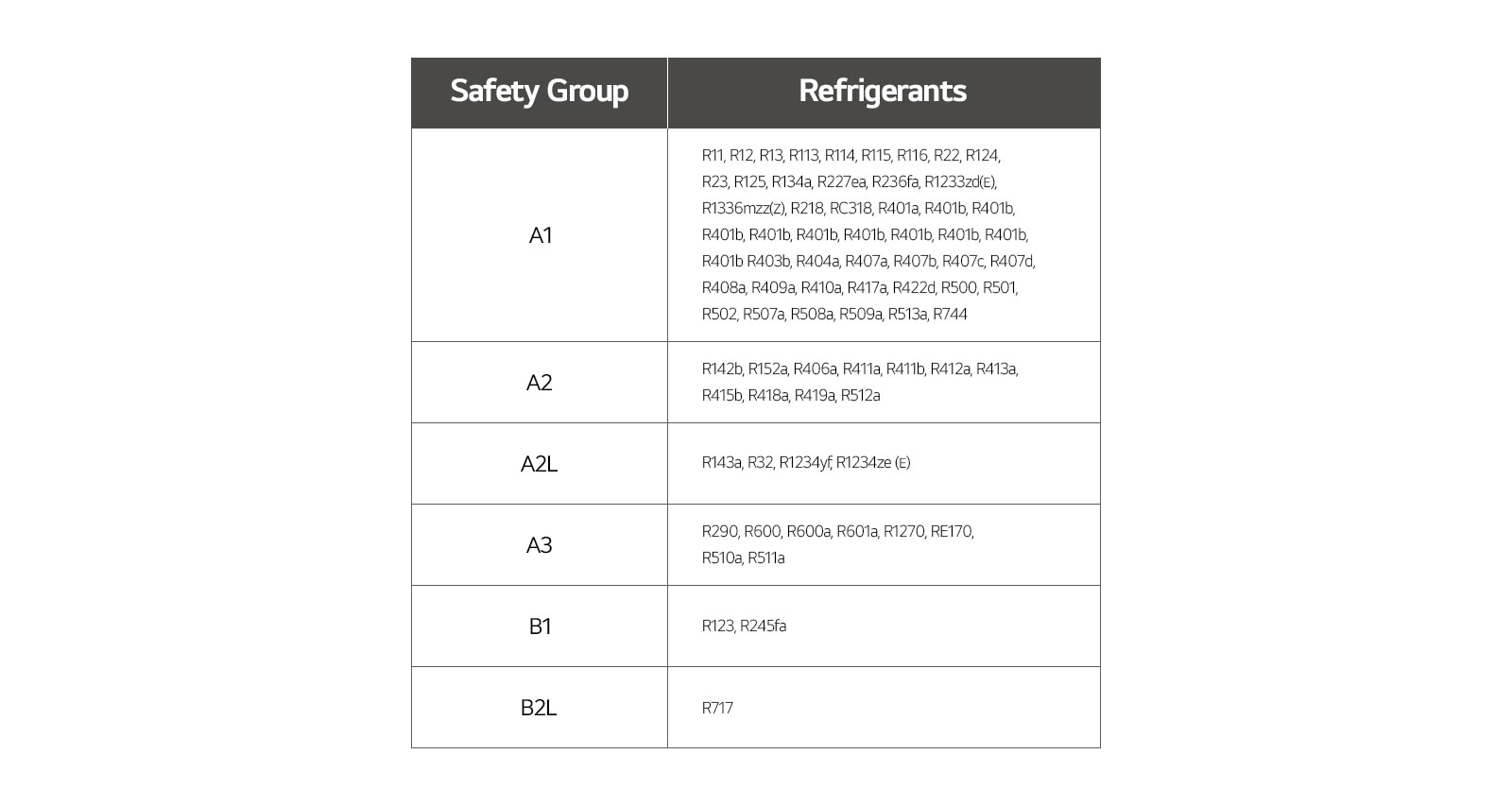
In order to effectively manage, maintain, and comply with regulatory requirements, industry professionals need to possess a thorough understanding of the safety aspects related to refrigerants. As long as the refrigerants are at a safe level, they are allowed to be used. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineering (ASHRAE) Standard 34, Designation and Safety Classification of Refrigerants has assigned numbers and safety qualifications to the refrigerants based on their toxicity and flammability.